For many investors, inflation-protected bonds – specifically designed to hedge against rising consumer prices – may be an effective way to seek to mitigate the impact of inflation. Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities, known as TIPS, are one of the most attractive members of this asset class.
What is inflation and why should I be concerned about it?
Inflation is an increase in the price of goods and services and, in effect, shrinks the value of your money. The dollar you invest today will be less valuable tomorrow, posing a serious threat to investors. Inflation is particularly concerning for bondholders since it can erode the purchasing power of future interest and principal payments.
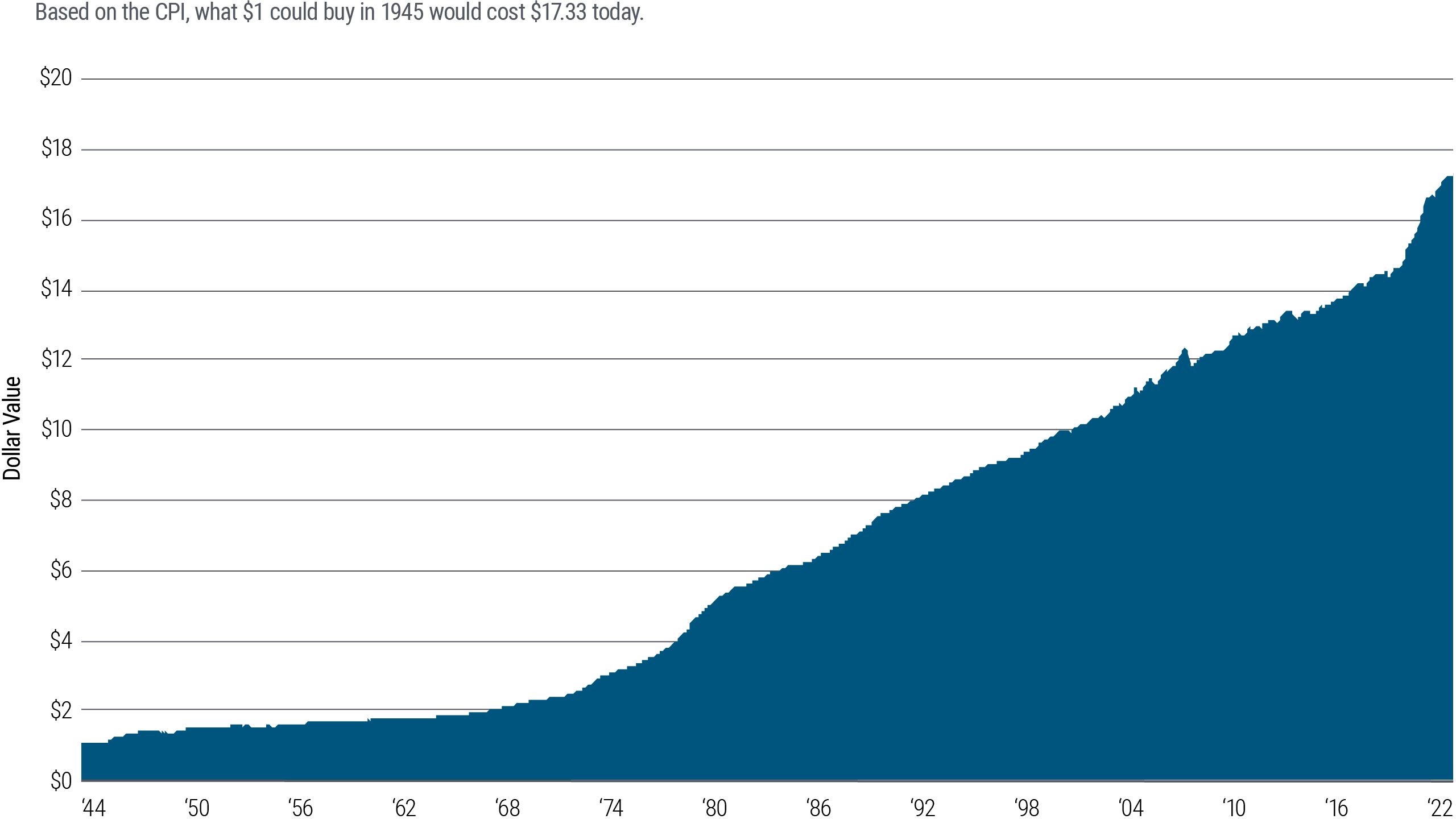
In the United States, a widely accepted measure of inflation is the Consumer Price Index (CPI). As the chart below shows, prices have risen steadily in the United States since the end of World War II, signaling a rise in inflation.
What are TIPS?
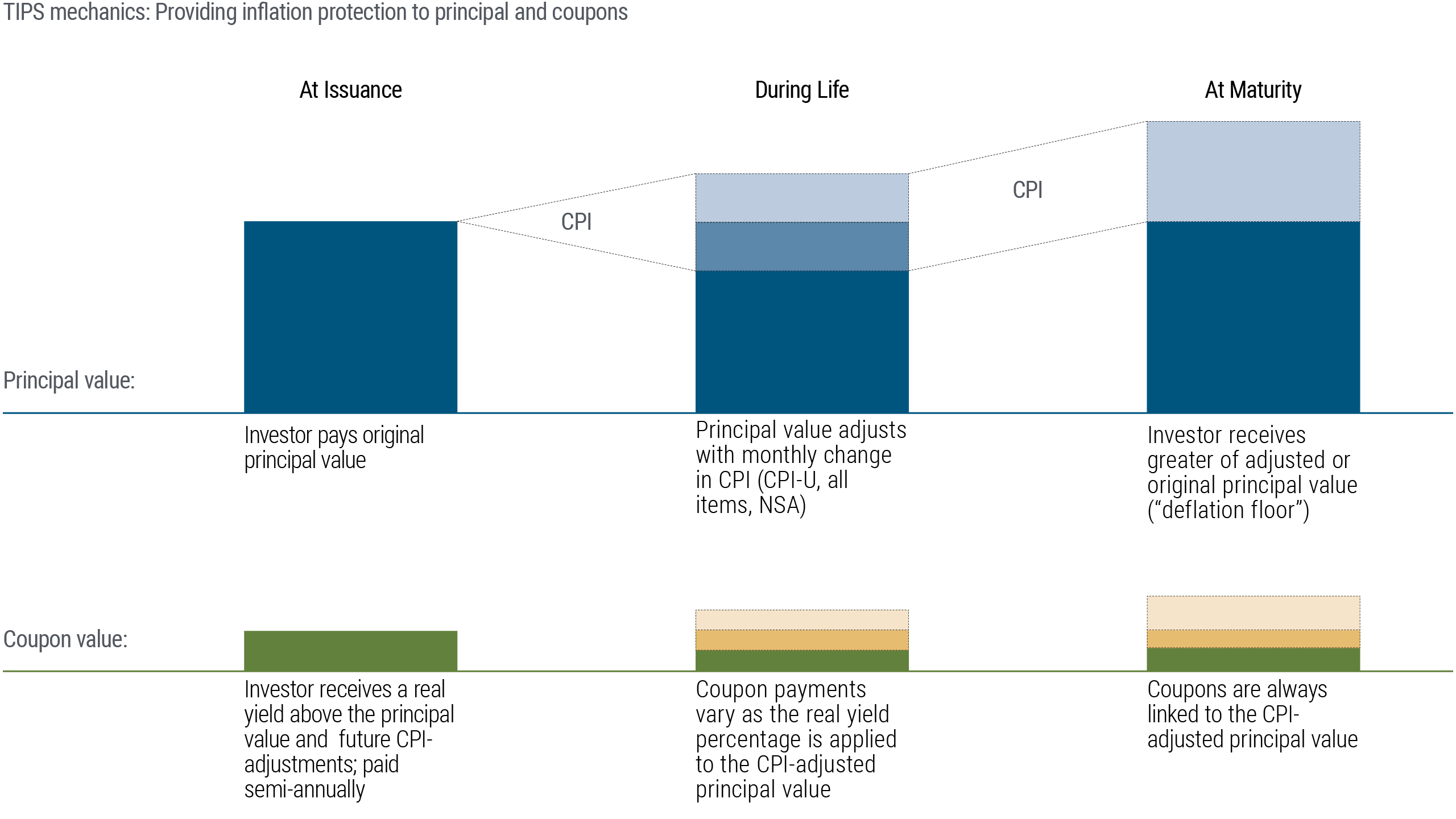
Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities, or TIPS, are inflation-protected bonds (IPBs) that are issued by the U.S. Treasury. Their face value is pegged to the CPI and adjusted in step with changes in the rate of inflation. The Treasury then pays interest on the adjusted face value of the bond, creating a gradually rising stream of interest payments if inflation continues to rise. At maturity, a TIPS investor will receive the original face value plus the sum of all the inflation adjustments since the bond was issued.
It works like this: Suppose you invest $1,000 in a new 10-year TIPS with a 2% coupon rate. If inflation is 3% over the next year, the face value will be changed to $1,030 and the annual interest payment would be $20.60, or 2% (the coupon rate) of the adjusted principal and so on. In a deflationary environment, the reverse would be true: the face value and interest payments would decrease, but still keep pace with the now lower cost of goods and services.
As a result, TIPS and other IPBs offer a “real” rate of return – the actual return of an investment after inflation is taken into account. A traditional bond, on the other hand, offers a “nominal” return. It maintains a fixed face value until maturity, with no adjustments for inflation. For example, if you’re receiving a 5% return on a traditional bond and inflation is rising at 3%, your “real” return is actually only 2%.
What are the benefits of investing in TIPS?
- TIPS can potentially be an effective portfolio diversification tool. Since TIPS have a low correlation with other types of investments, they may reduce overall portfolio volatility.
- TIPS offer the U.S. government’s assurance that investors will never receive less than the original face value of the bond at maturity, even in the event of deflation during the life of the bond.
What are the risks of TIPS compared with other bonds?
TIPS do not carry traditional credit risk thanks to their U.S. government guarantee but, like all bonds, TIPS are subject to interest rate risk. TIPS are expected to perform better in a rising interest rate environment than conventional U.S Treasury bonds because their inflation adjustments provide potential price support, but only when rates are rising because of increasing inflation. If rates were to rise in an environment of low or no inflation, TIPS’ prices could decline.
Investors who purchase individual TIPS should be aware of a phenomenon called “phantom income” – TIPS inflation adjustment to the face value of the bond is taxable in the year it occurs even though you won’t receive the bond’s full value until it matures. This differs from a mutual fund, which pays out both interest income and the income from principal adjustments to investors monthly. You pay the federal income tax, of course, but you’re also receiving the income you’re paying it on.
Investors who own TIPS through a mutual fund should also be aware that the fund may perform differently than the underlying bonds. Individual TIPS guarantee an inflation-adjusted return if held to maturity, but there is no guarantee for a fund; a portfolio manager may buy or sell TIPS before maturity, which could lead to gains or losses.
How can I invest in TIPS?
You can purchase TIPS directly from the U.S. Treasury for a minimum purchase amount of $1,000. You may also choose a mutual fund or exchange-traded fund that invests in TIPS, which offers the additional benefits of professional management. Your investment professional can help you decide which investment is right for you.